mirror of
https://github.com/seaweedfs/seaweedfs.git
synced 2024-11-23 18:49:17 +08:00
Page:
Cloud Drive Benefits
Pages
AWS CLI with SeaweedFS
AWS IAM CLI
Actual Users
Amazon IAM API
Amazon S3 API
Applications
Async Backup
Async Filer Metadata Backup
Async Replication to Cloud
Async Replication to another Filer
Benchmark SeaweedFS as a GlusterFS replacement
Benchmarks from jinleileiking
Benchmarks
Cache Remote Storage
Choosing a Filer Store
Client Libraries
Cloud Drive Architecture
Cloud Drive Benefits
Cloud Drive Quick Setup
Cloud Monitoring
Cloud Tier
Components
Configure Remote Storage
Customize Filer Store
Data Backup
Data Structure for Large Files
Deployment to Kubernetes and Minikube
Directories and Files
Docker Compose for S3
Docker Image Registry with SeaweedFS
Environment Variables
Erasure Coding for warm storage
Error reporting to sentry
FAQ
FIO benchmark
FUSE Mount
Failover Master Server
Filer Active Active cross cluster continuous synchronization
Filer Cassandra Setup
Filer Change Data Capture
Filer Commands and Operations
Filer Data Encryption
Filer JWT Use
Filer Metadata Events
Filer Redis Setup
Filer Server API
Filer Setup
Filer Store Replication
Filer Stores
Filer as a Key Large Value Store
Gateway to Remote Object Storage
Getting Started
HDFS via S3 connector
Hadoop Benchmark
Hadoop Compatible File System
Hardware
Hobbyest Tinkerer scale on premises tutorial
Home
Independent Benchmarks
Kubernetes Backups and Recovery with K8up
Large File Handling
Load Command Line Options from a file
Master Server API
Migrate to Filer Store
Mount Remote Storage
Optimization
Path Specific Configuration
Path Specific Filer Store
Production Setup
Replication
Run Blob Storage on Public Internet
Run Presto on SeaweedFS
S3 API Audit log
S3 API Benchmark
S3 API FAQ
S3 Bucket Quota
S3 Nginx Proxy
SRV Service Discovery
SeaweedFS Java Client
SeaweedFS in Docker Swarm
Security Configuration
Security Overview
Server Startup Setup
Store file with a Time To Live
Super Large Directories
System Metrics
TensorFlow with SeaweedFS
Tiered Storage
UrBackup with SeaweedFS
Use Cases
Volume Files Structure
Volume Management
Volume Server API
WebDAV
Words from SeaweedFS Users
fstab
nodejs with Seaweed S3
rclone with SeaweedFS
restic with SeaweedFS
run HBase on SeaweedFS
run Spark on SeaweedFS
s3cmd with SeaweedFS
weed shell
18
Cloud Drive Benefits
Chris Lu edited this page 2024-05-23 09:01:23 -07:00
Introduction
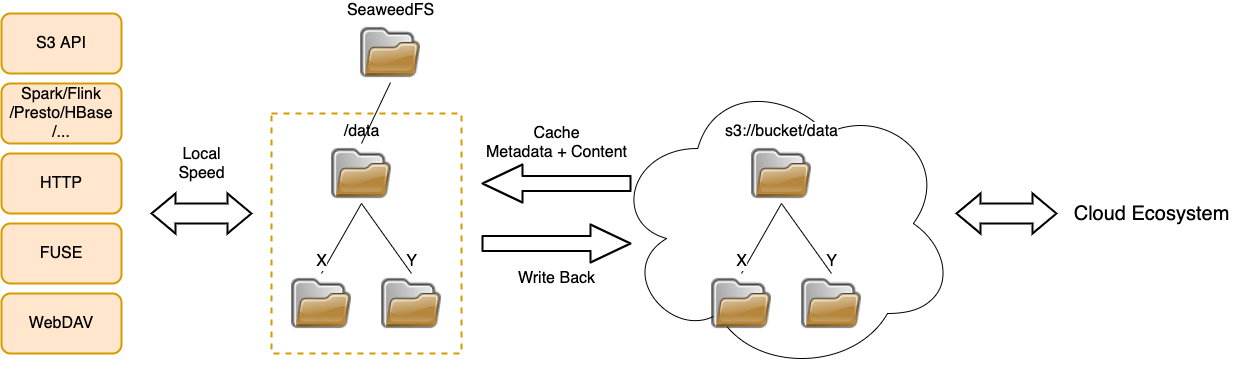
SeaweedFS provides two mechanisms to use cloud storage:
- SeaweedFS Cloud Drive (<== You are here)
- in this case, you can mount an S3 bucket to the Seaweedfs file system (in the filer), and access the remote files through SeaweedFS. Effectively, SeaweedFS caches the files from the cloud storage.
- In this mode, the file structure in cloud store is exactly matching the SeaweedFS structure - so every file in SeaweedFS will also become a file in the cloud storage provider.
- This is useful in case you want to use the files inside the cloud provider's infrastructure.
- However, this does not support file encryption in any way (obviously), as the files are put to Cloud Storage as is.
- Tiered Storage with Cloud Tier
- In this mode, seaweedFS moves full volume files to the cloud storage provider, so files which are 1 GB (in our case) big.
- This mode supports Filer Data Encryption transparently.
- The chunk files uploaded to the cloud provider are not usable outside of SeaweedFS.
Cloud is not for everyone
Nowadays, the industrial trend is to go to cloud storage, since "everybody is doing it". But after really using cloud storage, many users will find out:
- The cloud cost is too high. On AWS S3, the storage cost is relatively cheap (but not really) around $0.023 per GB per month. But accessing your own data is not cheap:
- API cost for PUT, POST, LIST requests is $0.005 per 1000 requests
- Transfer out cost is $0.09 per GB.
- The network latency is high and not consistent.
- Any code changes may increase your total cost.
- It limits engineers' creativity and development speed in order to watch for cost.
SeaweedFS can be a good choice
SeaweedFS can be good because:
- Freedom to read your own data! Any times that you want!
- Freedom to develop new features with fixed cost.
- Free to use faster high-capacity storage hardware.
- Local access latency.
- Avoid noisy neighbor problem.
- Cross data center replication gives high data redundancy and availability.
However, how to make SeaweedFS work with data already on cloud?
Design
Benefits
- Minimum Transfer Cost
- Download existing data only once.
- Updates are uploaded for free.
- Cached Locally
- Fast metadata operations.
- Fast read and write at local network latency and throughput.
- Fast and cheaper hardware.
- Avoid noisy neighbors.
- Scalable Capacity
- Just cache everything.
- No cache churn.
- Easy To Manage
- Warm up cache for by folder, file name pattern, file size, file age, etc.
- Uncache by folder, file name pattern, file size, file age, etc.
- Optionally write data back to cloud storage.
- One system for both remote storage cache and local storage.
- Flexible
- Work with existing cloud ecosystems.
- Can transparently switch to different cloud storage vendors.
- Can detach from the cloud storage if decided to move off cloud.
What SeaweedFS Cloud Drive is not?
- It is not a proxy. Proxy is not ideal for low-latency read or write operations.
- Its cache size is not limited. With unlimited size, all file content can be localized. So the read can be fast even on the first attempt, without worrying cached items are evicted due to capacity.
- Its cache is not write-through, which is slower than write-back. Usually local changes are asynchronously write back to the cloud within seconds.
- It does not change file storage layout in the cloud storage. So other tools can access the files on the cloud storage as usual.
- It does not need to link to the original cloud storage. After caching all the file content, you can choose to detach from the cloud storage.
Why SeaweedFS Cloud Drive?
There are other products also cache S3 data. What makes SeaweedFS Cloud Drive better?
SeaweedFS Cloud Drive has these unique characteristics:
- No change to existing workflow
- No directory or file format changes on cloud storage.
- Scalable Capacity
- Easy to add more capacity.
- Disaggregated storage.
- Tiered storages with NVME/SSD/HDD.
- Easy to manage
- With unlimited capacity, no complicated caching strategy. Data can be fast on first read.
- No unexpected cache evictions.
- Can explicitly cache or uncache files by folder, name pattern, size, age, etc.
- Flexible
- Mounted folders can become normal folders. Just stop writing back to the cloud.
- Transparently move data between vendors.
Possible Use Cases
Machine learning
- Problem
- Training jobs need to repeatedly visit a large set of files.
- The randomized access pattern is hard for caching.
- With SeaweedFS Cloud Drive
- Users can explicitly ask SeaweedFS Cloud Drive to cache one whole folder.
- Increase training speed and reduce API cost and network cost.
- Users can access data with FUSE mounted folders.
Data Hoarding
- Problem
- Local storage is not reliable enough.
- With cloud capacity, reliability, and storage tiering, saving data files there may be a good idea.
- Accessing cloud data is slow and costly.
- Recently uploaded files very likely need to be accessed again.
- With SeaweedFS Cloud Drive
- The local copy and remote copy can be backup for each other, if users choose not to uncache.
- To keep recent data in local copy, users can choose to only uncache files older than a limit.
Big Data
- Problem
- Run MapReduce, Spark, and Flink jobs on cloud data is slow due to metadata operations.
- Repeated data access increases unnecessary cost.
- May need to work with the cloud ecosystem.
- With SeaweedFS Cloud Drive
- Avoiding slow cloud storage metadata access.
- Access data only once.
- Write back data to work with cloud ecosystems.
Cloud Storage Vendor Agnostic
- Problem
- Different datasets may need to be on different vendors, based on access pattern, latency, cost, etc.
- With SeaweedFS Cloud Drive
- Transparently switch to from one vendor to another.
Switch S3 Compatible Storage Vendors
- Problem
- Other S3 compatible vendors are known to have lesser flexibility, scalability and performance as SeaweedFS.
- With SeaweedFS Cloud Drive
- Compare SeaweedFS with the vendor over a long period of time.
- Transparently switch away if SeaweedFS works better.
Move Off Cloud
- Problem
- Cloud storage is costly!
- With SeaweedFS Cloud Drive
- Help to transition between on-cloud to off-cloud.
- When you are happy with it, just stop the write back process (and cancel the monthly payment to the cloud vendor!).
Support multiple access methods.
- Problem
- You may need to access cloud data by HDFS, or HTTP, or S3 API, or WebDav, or FUSE Mount.
- With SeaweedFS Cloud Drive
- Multiple ways to access remote storage.
Introduction
API
Configuration
- Replication
- Store file with a Time To Live
- Failover Master Server
- Erasure coding for warm storage
- Server Startup Setup
- Environment Variables
Filer
- Filer Setup
- Directories and Files
- Data Structure for Large Files
- Filer Data Encryption
- Filer Commands and Operations
- Filer JWT Use
Filer Stores
- Filer Cassandra Setup
- Filer Redis Setup
- Super Large Directories
- Path-Specific Filer Store
- Choosing a Filer Store
- Customize Filer Store
Advanced Filer Configurations
- Migrate to Filer Store
- Add New Filer Store
- Filer Store Replication
- Filer Active Active cross cluster continuous synchronization
- Filer as a Key-Large-Value Store
- Path Specific Configuration
- Filer Change Data Capture
FUSE Mount
WebDAV
Cloud Drive
- Cloud Drive Benefits
- Cloud Drive Architecture
- Configure Remote Storage
- Mount Remote Storage
- Cache Remote Storage
- Cloud Drive Quick Setup
- Gateway to Remote Object Storage
AWS S3 API
- Amazon S3 API
- AWS CLI with SeaweedFS
- s3cmd with SeaweedFS
- rclone with SeaweedFS
- restic with SeaweedFS
- nodejs with Seaweed S3
- S3 API Benchmark
- S3 API FAQ
- S3 Bucket Quota
- S3 API Audit log
- S3 Nginx Proxy
- Docker Compose for S3
AWS IAM
Machine Learning
HDFS
- Hadoop Compatible File System
- run Spark on SeaweedFS
- run HBase on SeaweedFS
- run Presto on SeaweedFS
- Hadoop Benchmark
- HDFS via S3 connector
Replication and Backup
- Async Replication to another Filer [Deprecated]
- Async Backup
- Async Filer Metadata Backup
- Async Replication to Cloud [Deprecated]
- Kubernetes Backups and Recovery with K8up
Messaging
Use Cases
Operations
Advanced
- Large File Handling
- Optimization
- Volume Management
- Tiered Storage
- Cloud Tier
- Cloud Monitoring
- Load Command Line Options from a file
- SRV Service Discovery
- Volume Files Structure