Table of Contents
Cloud storage options, such as Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, Azure, Backblaze B2, etc, are ideal for backup purpose.
For example, for Amazon S3, the upload is free. You only pay for the storage. So you have the benefit of:
- Extremely fast access to local SeaweedFS Filer
- Near-Real-Time Backup to Amazon S3 with zero-cost upload network traffic.
Of course, you can also backup to local disks on another machine.
Architecture
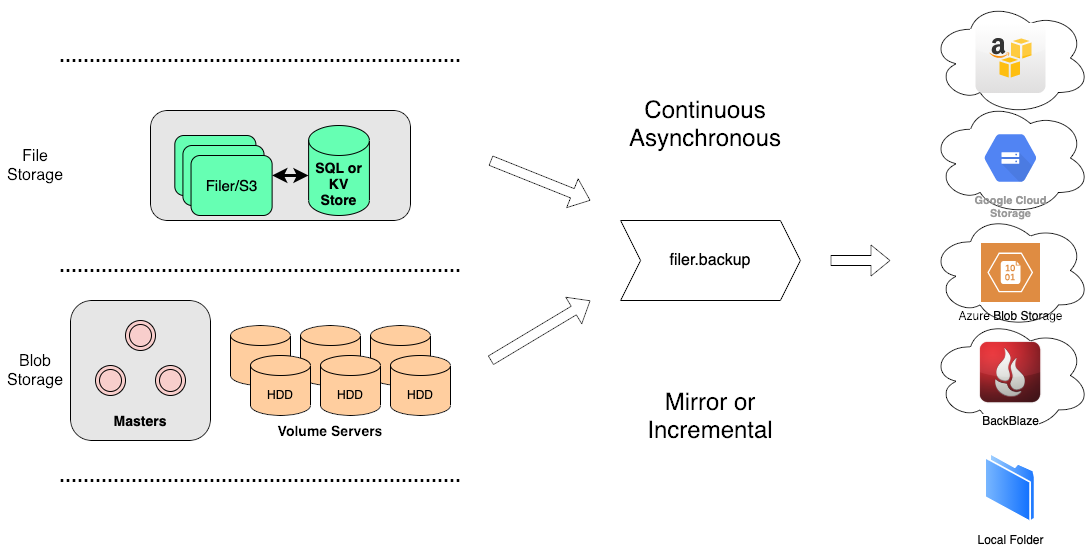
All file meta data changes in Filer are saved in the logs and can be subscribed. See Filer Change Data Capture. A "weed filer.backup" process will subscribe to this topic, and then read the actual file content, and send the update to the cloud sink or local disk sinks.
- Sinks can be: AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage, Microsoft Azure, Backblaze B2, or Local Disk.
Configuration
This command replaced the previous weed filer.replicate, which requires an external message queue.
But for configuration, use the same weed scaffold -config=replication to generate a replication.toml file. Just need to keep the lines of the sinks that you want to use.
[sink.s3]
# read credentials doc at https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sdk-for-go/v1/developer-guide/sessions.html
# default loads credentials from the shared credentials file (~/.aws/credentials).
enabled = false
aws_access_key_id = "" # if empty, loads from the shared credentials file (~/.aws/credentials).
aws_secret_access_key = "" # if empty, loads from the shared credentials file (~/.aws/credentials).
region = "us-east-2"
bucket = "backupbucket" # an existing bucket
directory = "/" # destination directory
endpoint = "http://localhost:8334"
is_incremental = false
Running Backup
- Make sure the
replication.tomlis in place. - Start the backup by running
weed filer.backup.
Unless interrupted, the weed filer.backup will run continuously and keep retrying if any error happens.
The weed filer.backup process can also be stopped at any time. The current backup progress, which is the "offset" for normal message queues, is stored on filer with the key as <sink_name, sink_folder>. So to resume, you can just restart, or even start from another server, as long as you have the same replication.toml file
Backup Strategies
There are 2 backup strategies supported as of now:
- Continuously mirrored changes. All the content are stored with the same directory structure as the source, but in a remote machine or a cloud vendor.
- Differential Incremental mode. New or updated content are stored in its folder named as modified date. Deletions are not applied.
Incremental Mode
If is_incremental = true, all the files are backed up under the YYYY-MM-DD directories, which the timestamps are based on modified time.
So
- Each date directory contains all new and updated files.
- The deleted files in the source filer will not be deleted on the backup.
So if in this folder, on 2021-03-01, these files are created in the source:
/dir1/file1
/dir1/file2
/dir1/file3
and on 2021-03-02, these files are created, modified, deleted in the source:
/dir1/file1 // modified
/dir1/file2 // not changed
/dir1/file3 // deleted
/dir1/file4 // created
The backup destination will have the following directory structure.
/2021-03-01/dir1/file1
/2021-03-01/dir1/file2
/2021-03-01/dir1/file3
/2021-03-02/dir1/file1
/2021-03-02/dir1/file4
Introduction
API
Configuration
- Replication
- Store file with a Time To Live
- Failover Master Server
- Erasure coding for warm storage
- Server Startup Setup
- Environment Variables
Filer
- Filer Setup
- Directories and Files
- Data Structure for Large Files
- Filer Data Encryption
- Filer Commands and Operations
- Filer JWT Use
Filer Stores
- Filer Cassandra Setup
- Filer Redis Setup
- Super Large Directories
- Path-Specific Filer Store
- Choosing a Filer Store
- Customize Filer Store
Advanced Filer Configurations
- Migrate to Filer Store
- Add New Filer Store
- Filer Store Replication
- Filer Active Active cross cluster continuous synchronization
- Filer as a Key-Large-Value Store
- Path Specific Configuration
- Filer Change Data Capture
FUSE Mount
WebDAV
Cloud Drive
- Cloud Drive Benefits
- Cloud Drive Architecture
- Configure Remote Storage
- Mount Remote Storage
- Cache Remote Storage
- Cloud Drive Quick Setup
- Gateway to Remote Object Storage
AWS S3 API
- Amazon S3 API
- AWS CLI with SeaweedFS
- s3cmd with SeaweedFS
- rclone with SeaweedFS
- restic with SeaweedFS
- nodejs with Seaweed S3
- S3 API Benchmark
- S3 API FAQ
- S3 Bucket Quota
- S3 API Audit log
- S3 Nginx Proxy
- Docker Compose for S3
AWS IAM
Machine Learning
HDFS
- Hadoop Compatible File System
- run Spark on SeaweedFS
- run HBase on SeaweedFS
- run Presto on SeaweedFS
- Hadoop Benchmark
- HDFS via S3 connector
Replication and Backup
- Async Replication to another Filer [Deprecated]
- Async Backup
- Async Filer Metadata Backup
- Async Replication to Cloud [Deprecated]
- Kubernetes Backups and Recovery with K8up
Metadata Change Events
Messaging
Use Cases
Operations
Advanced
- Large File Handling
- Optimization
- Volume Management
- Tiered Storage
- Cloud Tier
- Cloud Monitoring
- Load Command Line Options from a file
- SRV Service Discovery
- Volume Files Structure